Study Sheds New Light on Post-Operative Bleeding in Newborns
For Immediate Release
A new study finds significant differences between the blood clot structure in adults and newborns, helping researchers better understand the challenges in addressing post-operative bleeding in neonatal patients. The researchers also found that the current standard of care for treating post-operative bleeding may pose an increased risk of thrombosis in newborns compared to adults, which researchers hadn’t suspected. The study was performed by researchers at North Carolina State University, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Emory University, Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta and the Georgia Institute of Technology.
“We knew that neonates – infants less than one month old – are more likely than adults to suffer from severe bleeding after heart surgery, which poses a variety of health risks,” says Ashley Brown, first author of a paper on the study and an assistant professor in the joint biomedical engineering department at NC State and UNC-Chapel Hill.
“The current standard of care is to give neonatal patients blood products – such as a protein called fibrinogen – derived from adult blood,” Brown says. “But neonatal blood and adult blood aren’t the same; many of the components involved in clotting in newborns have differing levels of activity, or effectiveness, compared to the same components in adults. Our goal was to better understand how clotting in neonates differs from that in adults, so that we can move closer to developing more effective treatment strategies for these infants.”
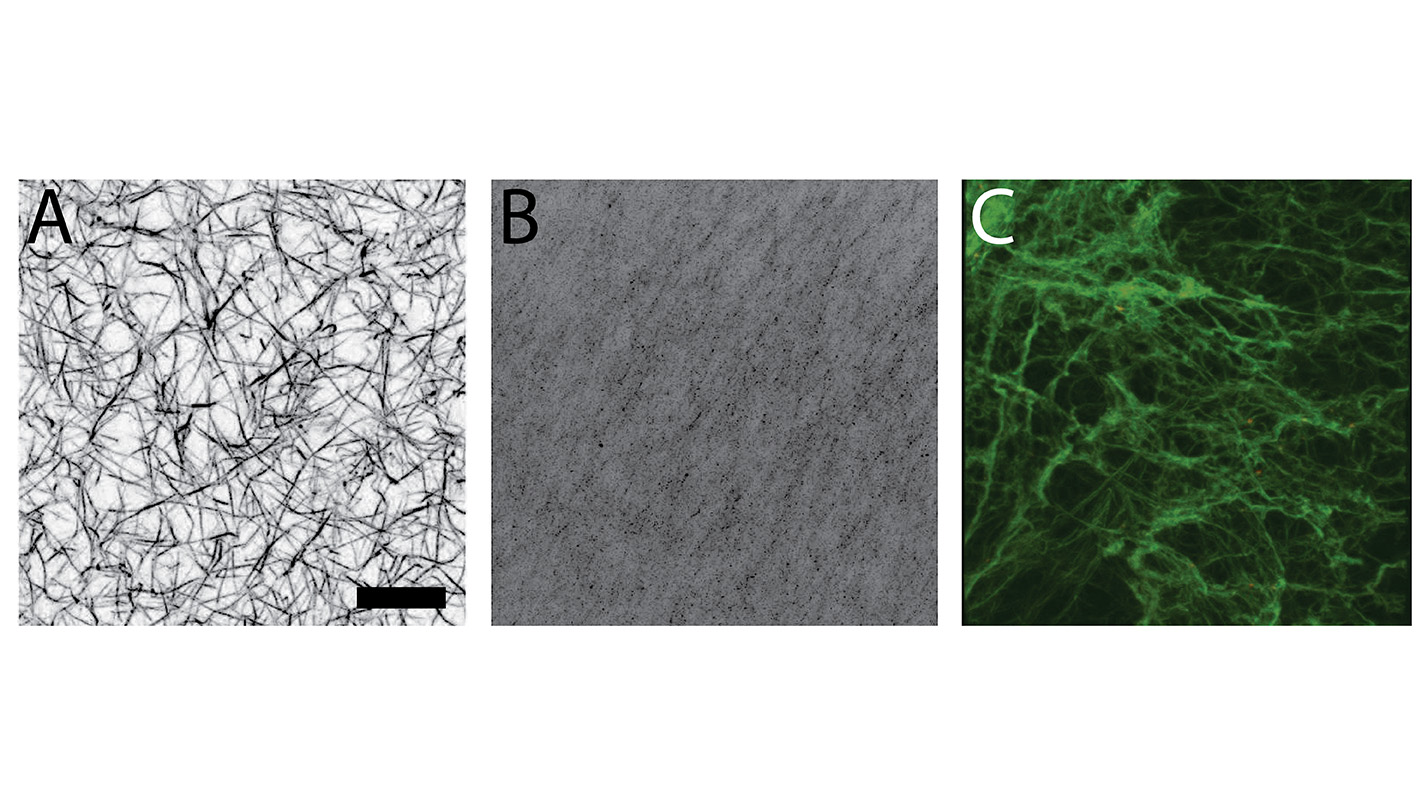
The researchers’ hypothesis was that fibrinogen – the main blood-clotting protein – from neonates would form clots that are different from those formed by adult fibrinogen, and they were correct. However, they were surprised to find that fibrinogen from adults did not integrate well with the fibrinogen in neonates. In other words, the fibrinogen from adults and newborns wouldn’t stick to each other and form a clot.
To test this hypothesis, the researchers took samples of neonate fibrinogen and adult fibrinogen and compared how they formed clots. They looked at clots formed solely of adult fibrinogen, clots formed solely of neonate fibrinogen, and clots formed of mixed adult and neonate fibrinogen.
The researchers found that neonate fibrinogen formed less dense, more fragile clots than adult fibrinogen. And they found that a mixture of adult and neonate fibrinogen formed clots that were also fragile and less dense – even if there was relatively little neonate fibrinogen in the mixture.
The researchers also evaluated how long it took these clots to dissolve. This is important because blood clots that don’t break down can form thrombosis or be released into the bloodstream and cause a stroke.
The study showed that clots of neonate fibrinogen dissolve about twice as quickly as clots formed from adult fibrinogen. It also showed that clots formed from an adult and neonate fibrinogen mixture dissolved at approximately the same rate as adult-only clots – regardless of the percentage of neonate fibrinogen in the mixture.
“This suggests that using adult fibrinogen in neonatal patients may pose an increased risk of embolism or other adverse thrombotic events,” says Nina Guzzetta, MD, corresponding author on the study, associate professor of anesthesiology at Emory University School of Medicine, and a pediatric cardiac anesthesiologist at Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta.
“This work drives home that newborns are not just small adults, and we still have much to learn about clotting in neonates,” Guzzetta says. “It also tells us that there is a great deal of room for improvement in the current standard of care for post-operative bleeding in neonates.
“We are investigating several approaches that may help address this problem, evaluating various modes of action,” Brown says. “It is possible that we can use various external factors that promote clotting to stimulate the fibrinogen in neonates to form a denser clot. We are investigating possible alternatives to help neonates form a better clot after major surgery without having to use adult fibrinogen. For example, we are investigating the use of synthetic platelet-like particles developed by our team to augment hemostasis – the biological process that stops bleeding – in blood samples collected from these patients.”
The paper, “Fibrin network changes in neonates after cardiopulmonary bypass,” was published online March 3 in the journal Anesthesiology. The paper was co-authored by Riley Hannan, now at the University of Virginia; Lucas Timmins and Thomas Barker of the biomedical engineering program at Georgia Tech and Emory; and Janet Fernandez of Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta. The work was supported by the Emory University and Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta Children’s Center for Cardiovascular Biology and by the National Institutes of Health under grant R21EB019068.
-shipman-
Note to Editors: The study abstract follows.
“Fibrin network changes in neonates after cardiopulmonary bypass”
Authors: Ashley C. Brown, North Carolina State University and University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill; Riley Hannan and Thomas H. Barker, Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University; Lucas H. Timmins, Emory University; Janet D. Fernandez, Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta; and Nina A Guzzetta, Emory University and Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta
Published: online March 3, Anesthesiology
DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001058
Abstract: Background: Quantitative and qualitative differences exist between the hemostatic systems of neonates and adults, among them the presence of ‘fetal’ fibrinogen, a qualitatively dysfunctional form of fibrinogen that exists until one year of age. The consequences of ‘fetal’ fibrinogen on clot structure in neonates, particularly in the context of surgical associated bleeding, have not been well characterized. Here we examine the sequential changes in clotting components and resultant clot structure in a small sample of neonates undergoing cardiac surgery and cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB).
Methods: Blood samples were collected from neonates (n=10) before surgery, immediately after CPB and following the transfusion of cryoprecipitate (i.e. adult fibrinogen component). Clots were formed from patient samples or purified neonatal and adult fibrinogen. Clot structure was analyzed using confocal microscopy.
Results: Clots formed from plasma obtained after CPB and after transfusion were more porous than baseline clots. Analysis of clots formed from purified neonatal and adult fibrinogen, demonstrated that at equivalent fibrinogen concentrations, neonatal clots lack three-dimensional structure while adult clots were denser with significant three-dimensional structure. Clots formed from a combination of purified neonatal and adult fibrinogen were less homogenous than those formed from either purified adult or neonatal fibrinogen.
Conclusions: Our results confirm that significant differences exist in clot structure between neonates and adults, and that neonatal and adult fibrinogen may not integrate well. These findings suggest that differential treatment strategies for neonates should be pursued to reduce the demonstrated morbidity of blood product transfusion.
- Categories:


