Researchers Find Diffusion Plays Unusual Signaling Role in Drosophila Embryos
For Immediate Release
Researchers from North Carolina State University have found that diffusion plays an unexpected role in cell differentiation during the early stages of development in the embryos of Drosophila, or fruit flies. Instead of spreading a molecular signal out, it was found that diffusion, facilitated through a carrier molecule, actually concentrates the signal in one place. This “facilitated diffusion” mechanism has previously been found in other systems, and the new finding indicates it may be more widespread than previously thought.
The development of Drosophila takes place quickly, with only 24 hours passing from the moment of fertilization until a larva emerges from the egg. For this study, researchers focused on a two-hour window of development, from the beginning of the second hour to the end of the third hour. At the beginning of this stage, the embryo consists of one large cell, with approximately 500 nuclei surrounding the yolk. By the end of the third hour, the embryo consists of about 8,000 nucleated cells – still surrounding the yolk.
“These 8,000 cells are starting to differentiate – some are becoming neurons while others will be skin cells, and so on,” says Greg Reeves, an assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at NC State and corresponding author of a paper on the work. “What we looked at is how the developing embryo sends signals to all of these cells so that they know to differentiate.”
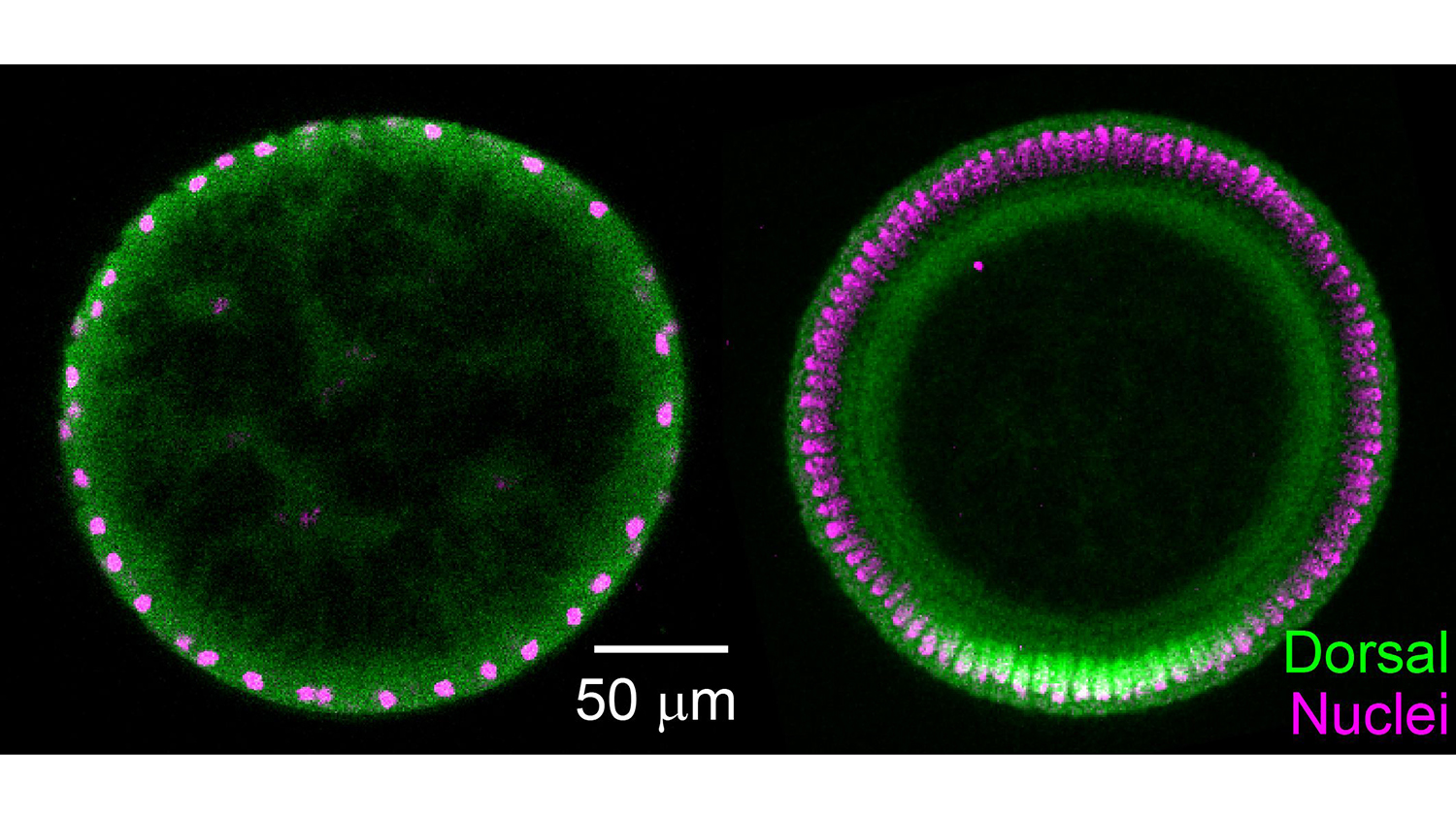
During early stages of development, embryos transmit signals to cells along two gradients that are basically latitudinal and longitudinal. The combination of both signals tells cells what they will develop into. At issue in this paper are the Dorsal gradient signals, which are transcription factors. Transcription factors are proteins that bind to DNA in a nucleus and regulate gene expression. Because the nuclei at this stage of development aren’t separated by cell walls, these Dorsal proteins can shuttle easily from place to place along the periphery of the embryo.
But these Dorsal proteins are kept inactive by an inhibitory protein called Cactus, which binds to Dorsal – forming a Dorsal-Cactus complex that can’t enter a nucleus.
In order to do their job, Dorsal proteins rely on Toll proteins, which trigger a cascade that ultimately degrades Cactus – freeing Dorsal proteins to enter a nucleus and bind with DNA. And Toll proteins, in turn, only begin doing their jobs along the ventral side of the embryo.
That description has been the longstanding explanation of how this process works – but Reeves and his team have now shown that there is more to it.
In this case, the researchers have found that diffusion plays a key role – but not necessarily the role they were anticipating.
“Usually, the signal starts at one place, then diffuses out to create the gradient,” Reeves explains. “What happens here is essentially the opposite of that.”
Specifically, as Toll degrades the Cactus, allowing Dorsal to enter nuclei, it creates an imbalance: there are more Dorsal-Cactus complexes on one side of the embryo than on the other. This leads additional Dorsal-Cactus complexes to migrate to the ventral side – via diffusion – in an attempt to restore balance.
“The net effect of the process is that more Dorsal are deposited on the ventral side,” Reeves says. “Cactus is not only an inhibitor, as we previously thought, it also serves as a carrier.
“The advantage of this facilitated diffusion mechanism is that it effectively amplifies the signal from the Dorsal proteins,” Reeves says.
And in embryos with a shortage of Dorsal proteins, the mechanism also concentrates Dorsal in the area where it is most important – increasing the likelihood that the embryo will be viable.
“This diffusion mechanism has previously been found in frogs and other independent systems,” Reeves says. “So finding it here suggests that it may be more prevalent than we thought. And if it is prevalent in nature, that may indicate an efficiency that could inform the development of techniques that could be used for applications such as drug delivery. It would be a long way off, but it’s worth looking into.”
The paper, “A facilitated diffusion mechanism establishes the Drosophila Dorsal gradient,” is published in the journal Development. Lead authors of the study are Sophia Carrell and Michael O’Connell, former Ph.D. students at NC State. Co-authors include Thomas Jacobsen, a Ph.D. student at NC State; Amy Pomeroy and Stephanie Hayes, former undergraduates at NC State; and Reeves. The work was done with support from the National Science Foundation, under grant number CBET-1254344, and the U.S. Department of Education, under grant numbers P200A100004, P200A140020 and P200A120047.
-shipman-
Note to Editors: The study abstract follows.
“A facilitated diffusion mechanism establishes the Drosophila Dorsal gradient”
Authors: Sophia N. Carrell, Michael D. O’Connell, Thomas Jacobsen, Amy E. Pomeroy, Stephanie M. Hayes and Gregory T. Reeves, North Carolina State University
Published: Nov. 2, Development
DOI: 10.1242/dev.155549
Abstract: The transcription factor NF-ϰB plays an important role in the immune system, apoptosis, and inflammation. Dorsal, a Drosophila homolog of NF-ϰB, patterns the dorsal-ventral axis in the blastoderm embryo. During this stage, Dorsal is sequestered outside the nucleus by the IϰB homolog Cactus. Toll signaling on the ventral side breaks the Dorsal/Cactus complex, allowing Dorsal to enter the nucleus to regulate target genes. Fluorescent data show that Dorsal accumulates on the ventral side of the syncytial blastoderm. Here we use both modeling and experiment to show that this accumulation is due to facilitated diffusion, or shuttling, of Dorsal/Cactus complex. We also show that active Toll receptors are limiting in wildtype embryos, which is a key factor in explaining global Dorsal gradient formation. Our results suggest that shuttling is necessary for viability of embryos from mothers with compromised dorsal levels. Therefore, Cactus not only has the primary role of regulating Dorsal nuclear import, but also a secondary role in shuttling. Given that this mechanism has been found in other, independent systems, we suggest it may be more prevalent than previously thought.
- Categories:


