Predators and Hidey-Holes Are Good for Reef Fish Populations

For Immediate Release
New research highlights two factors that play a critical role in supporting reef fish populations and – ultimately – creating conditions that are more favorable for the growth of both coral reefs and seagrass.
“Previous work has shown mixed results on whether the presence of large predator species benefits reef fish populations, but we found that the presence of Nassau grouper (Epinephelus striatus) had an overall positive effect on fish abundance,” says Enie Hensel, a former Ph.D. student at North Carolina State University and lead author of a paper on the work. “We also found that habitat complexity benefits both fish abundance and species richness, likely because it gives fish a larger variety of places to shelter.” This is consistent with previous work.
“One of the surprises here was that the effect of predator presence on fish abundance was comparable to the effect of habitat complexity,” Hensel says.
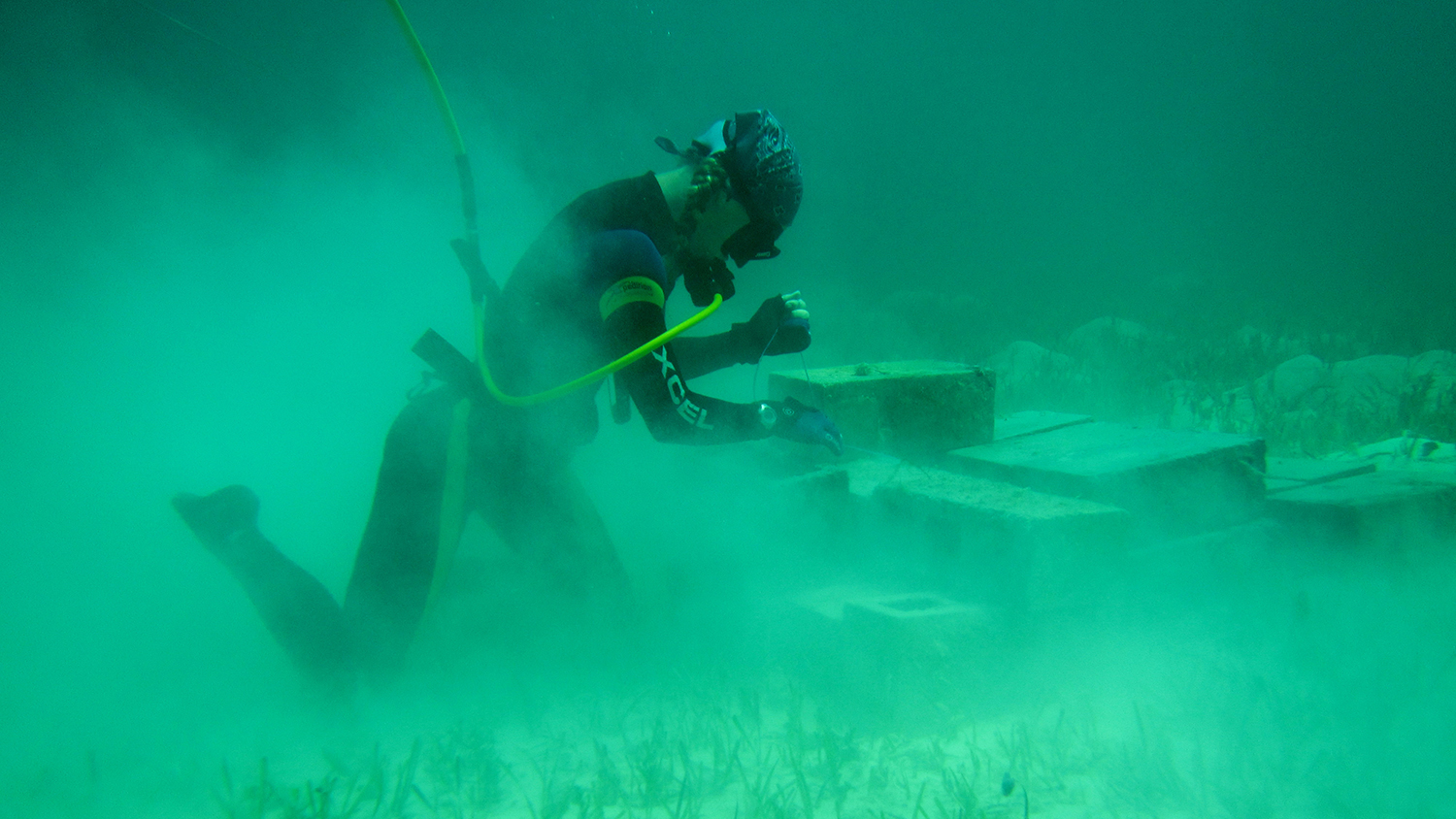
To better understand the effect of these variables, researchers constructed 16 artificial “patch” reefs in shallow waters off the coast of Great Abaco Island in The Bahamas. Eight of the reefs consisted of cement-filled cinder blocks, mimicking degraded reefs with limited habitat complexity. The remaining eight reefs consisted of unfilled cinder blocks and branching pipe structures, mimicking the more complex physical environment of healthier reefs.
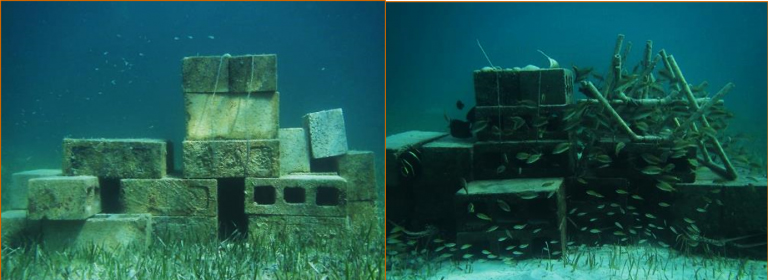
Once in place, the researchers waited for groupers to move in and claim the new reef territory. The groupers were large juveniles, ranging in size from 16-33 centimeters. The researchers then removed the groupers from four of the degraded reef sites and from four of the complex reef sites. Groupers that were removed were relocated to distant reefs.
Researchers monitored the sites for 60 days to ensure that the grouper-free reefs remained free of groupers. At the end of the 60 days, the researchers assessed the total number of fish at each reef site, as well as the total number of fish species at each site.
The differences were significant.
Fish abundance, or the total number of fish, was highest at sites that had both a resident grouper and complex habitat. Abundance at these sites ranged from 275 fish to more than 500 – which is remarkable given that each reef was less than a meter long in any direction. By comparison, sites that had simple structures and no grouper had fewer than 50 fish on average. Simple structures with predators had around 75 fish, while complex sites without grouper had around 100.
“We think the presence of the grouper drives away other predators, which benefits overall fish abundance,” Hensel says. “And a complex habitat offers niches of various sizes and shapes, which can shelter more and different kinds of fish than a degraded, simple habitat.”
The presence of grouper had little or no effect on species richness, or the number of different species present at each site. However, habitat complexity made a significant difference. Complex sites had 11-13 species, while degraded sites had around seven.
“We found that the sites with complex habitats and the presence of predators had fish populations that were actually larger than what we see at surrounding, similar-sized natural reefs,” Hensel says. “That’s because the natural reefs in the area are all degraded due to a variety of stressors.
“We also found that the presence of grouper on complex reefs led to a significant jump in the population of Tomtate grunts (Haemulon aurolineatum),” Hensel says. “That’s good news, because Tomtates are a species that provides a lot of ecosystem services, which would be good for creating conditions that are more amenable to both coral reef growth and seagrass growth.
“Currently, my colleagues and I are building from these findings in two directions. We’re measuring long-term community and ecosystem level responses to coral restoration or the reintroduction of structurally complex habitat; and we are also measuring long-term biological and physiological responses of fishes residing on restored reefs. For the latter, Haley Gambill, an undergraduate at NC State, is measuring changes in the age and growth of grunts.
“It’s also worth noting that this is an area that was hit hard by Hurricane Dorian. Because we’ve done so much reef population work in that area, I’m hoping to return to do some work that can help us understand how extreme weather events can affect these ecosystems.”
The paper, “Effects of predator presence and habitat complexity on reef fish communities in The Bahamas,” is published in the journal Marine Biology. The paper was co-authored by Jacob Allgeier of the University of Michigan; and Craig Layman, a former professor at NC State.
The work was done with support from the National Science Foundation under grants 0746164 and 1405198.
-shipman-
Note to Editors: The study abstract follows.
“Effects of predator presence and habitat complexity on reef fish communities in The Bahamas”
Authors: Enie Hensel and Craig A. Layman, North Carolina State University; Jacob E. Allgeier, University of Michigan
Published: Sept. 30, Marine Biology
DOI: 10.1007/s00227-019-3568-3
Abstract: Reef ecosystems are highly diverse habitats that harbor many ecologically and 26 economically significant species. Yet, globally they are under threat from multiple stressors 27 including overexploitation of predatory fishes and habitat degradation. While these two human-28 driven activities often occur concomitantly, they are typically studied independently. Using a 29 factorial design, we examined effects of predator presence, habitat complexity, and their 30 interaction on patch reef fish communities in a nearshore ecosystem on Great Abaco Island, The 31 Bahamas. We manipulated the presence of Nassau groupers (Epinephelus striatus), a reef 32 predator that is critically endangered largely due to overharvest, and varied patch reef structure 33 (cinder blocks with and without PVC) to reflect high or low complexity- four treatments in total. 34 To assess changes in fish community composition we measured fish abundances, species 35 richness, and evenness. We found that predators present and high reef complexity had an 36 additive, positive effect on total fish abundance: fish abundance increased by ~250% and 300%, 37 compared to predators absent and low complexity reef treatments, respectively. Species richness 38 increased with reef complexity. Variation in community structure was explained by the 39 interaction between factors, largely driven by juvenile Tomtate grunt (Haemulon aurolineatum) 40 abundances. Specifically, Tomtate grunt abundance was significantly higher on high complexity 41 reefs with predators present, but on low complexity reefs predators present had no effect on 42 Tomtate grunt abundance. Our data suggest that both fisheries management of large-bodied 43 piscivores and reef habitat restoration are critical to the management and conservation of reef 44 ecosystem functions and services.


